- GM's defensed unit sees $25 billion market in creating new products for the military based off its existing vehicles, parts and technologies.
- Future opportunities include electric powertrains and vehicles as well as autonomous systems and vehicles — focuses of its GM parent company.
- GM sold a previous defense unit with the same name to General Dynamics for $1.1 billion in 2003.
DETROIT – General Motors is targeting significant growth for its resurrected military defense unit, which quietly relaunched three years ago and recently started fulfilling its first major U.S. military contract.
GM sees a $25 billion market in creating new products for the military based off its existing vehicles, parts and technologies, according to Jeff Ryder, GM Defense vice president of growth and strategy.
"That's an addressable market that we feel we have a right to win and pursue. And that's what we're doing," he told CNBC. "As we mature, as we grow, as we build out our operating model, as we have more wins, we will have the opportunity, I think, to continue to vector into other directions or adjacent markets. So that number is not going to get smaller."
The company once built tanks for the military during WWII, but it has no plans to stretch that far from its core manufacturing, he said.
Ryder, an aerospace and defense industry veteran, said the military needs electric powertrains and vehicles as well as autonomous systems — focuses of its parent company. GM is investing $27 billion in such technologies through 2025.
Money Report
The Detroit automaker sold a previous defense unit with the same name to General Dynamics for $1.1 billion in 2003. Since relaunching GM Defense in 2017, the company has been ramping up the subsidiary and identifying appropriate military contracts to bid on.
Due to its current size, GM Defense has not gained much, if any, interest from Wall Street regarding valuation, but executives believe the opportunities for the unit are vast.
Batteries vs. fuel cells
When GM Defense was reestablished in 2017, it was expected to be a showcase for the automaker's fuel-cell technologies. But much like the consumer market, the demand wasn't yet there due to cost and lack of infrastructure.
Ryder said fuel cells remain part of the company's product offering, but GM Defense is now focusing on more near-term business opportunities, including battery-electric vehicles.
"The reality is the Army was not and is not yet ready to buy thousands of fuel-cell- powered vehicles," he said, adding "electric vehicles are a very, very real conversation right now."

Fuel-cell vehicles operate much like EVs but are powered by electricity generated from hydrogen and oxygen. Such vehicles emit only water while driving and are considered complementary and better for longer trips than battery-electric vehicles. The vehicles can operate on renewable hydrogen made from sources like wind and biomass.
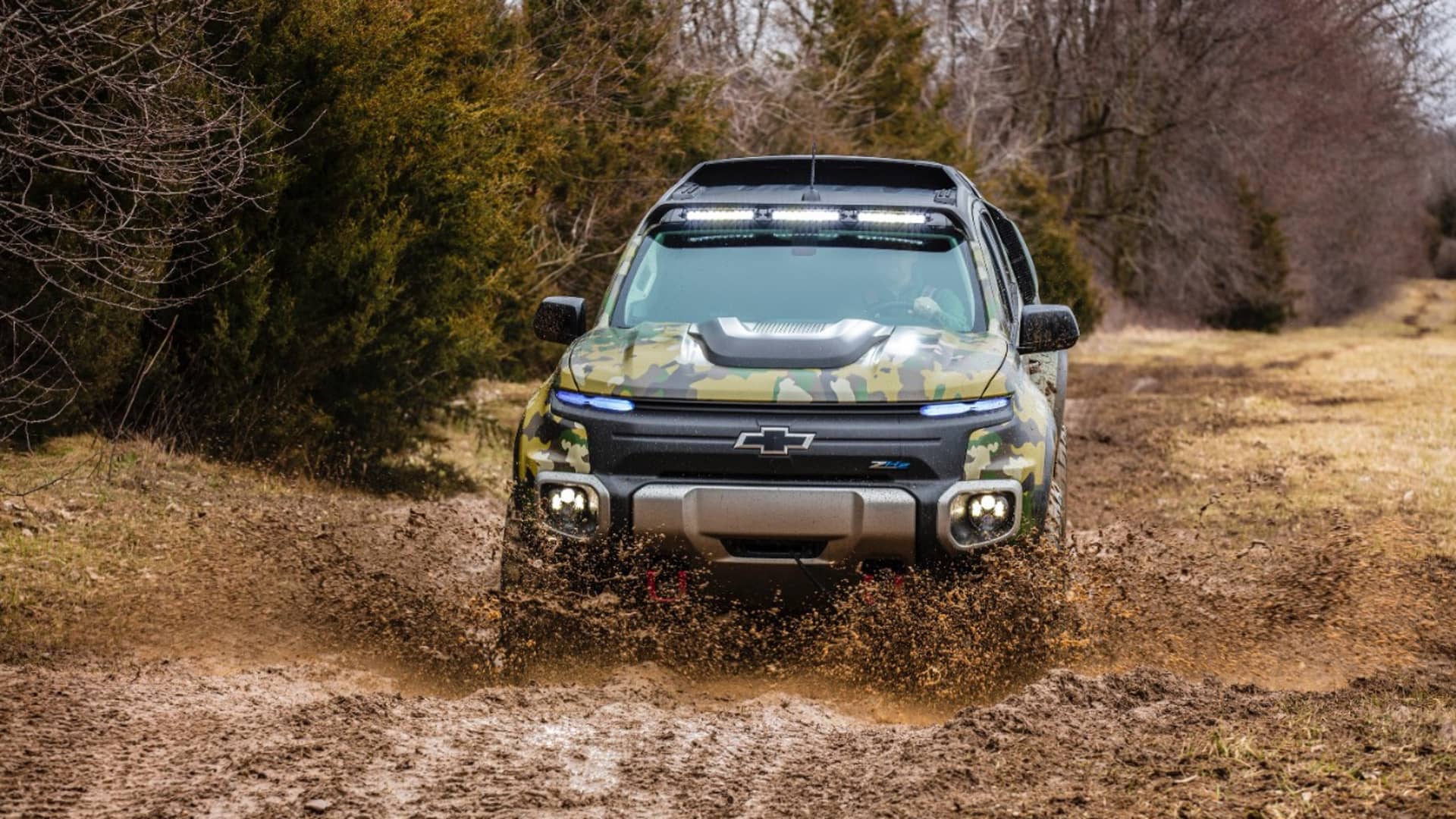
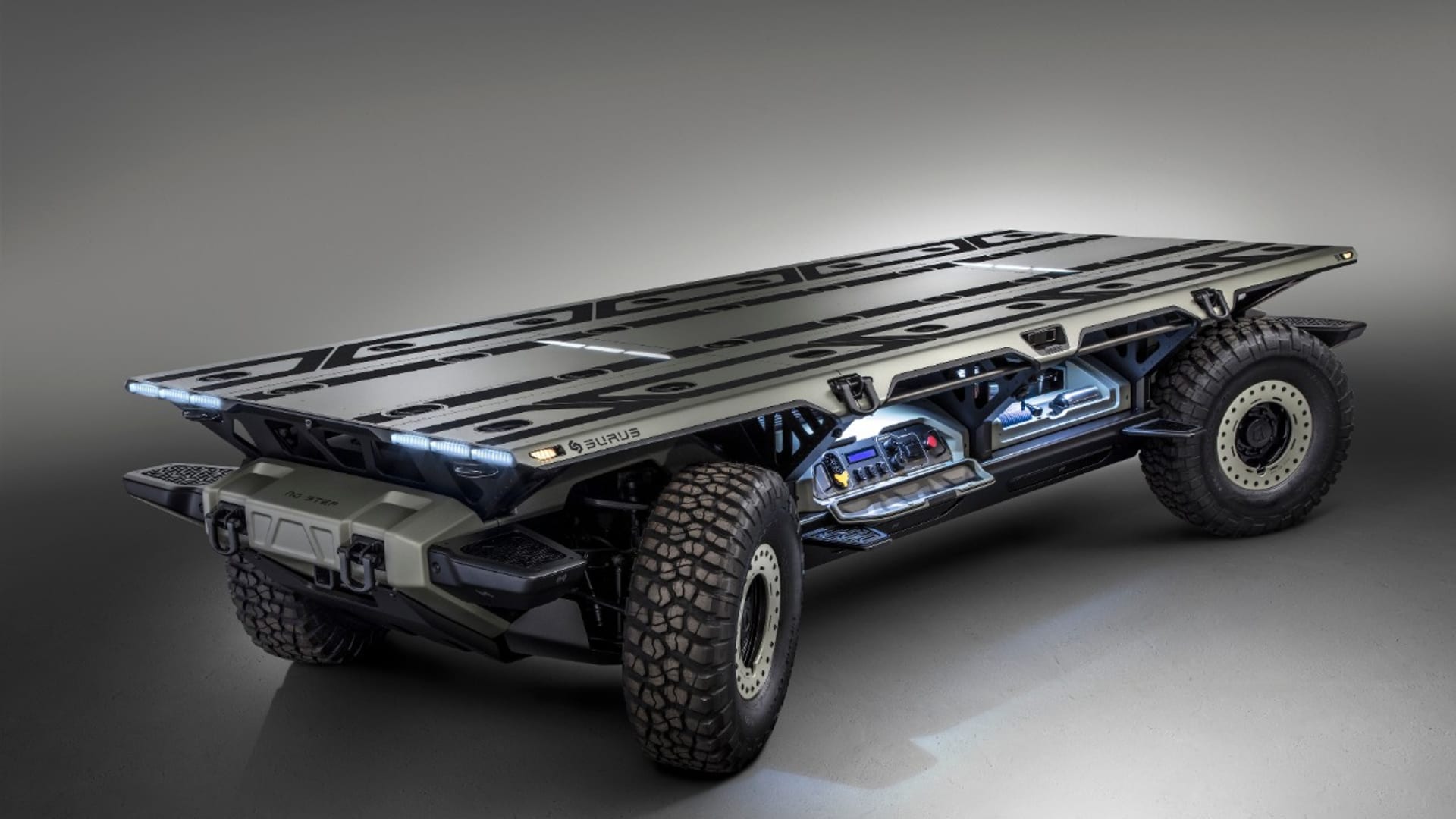
GM previously partnered with the U.S. defense industry for evaluation of fuel-cell products, including a Colorado-based pickup called the ZH2 and an unmanned undersea vehicle. The company also has showcased a military vehicle platform called the Silent Utility Rover Universal Superstructure as a proof of its fuel-cell technologies.
Some advantages EVs and fuel cells offer over gasoline- and diesel-powered vehicles is its near-instantaneous torque to move quickly as well as lack of noise and thermal detection, according to Ryder.

$214 million contract
Until the U.S. military is ready to largely adopt such technologies, GM Defense is focusing its near-term operations on vehicles with internal combustion engines as well as more traditional powertrains and technologies.
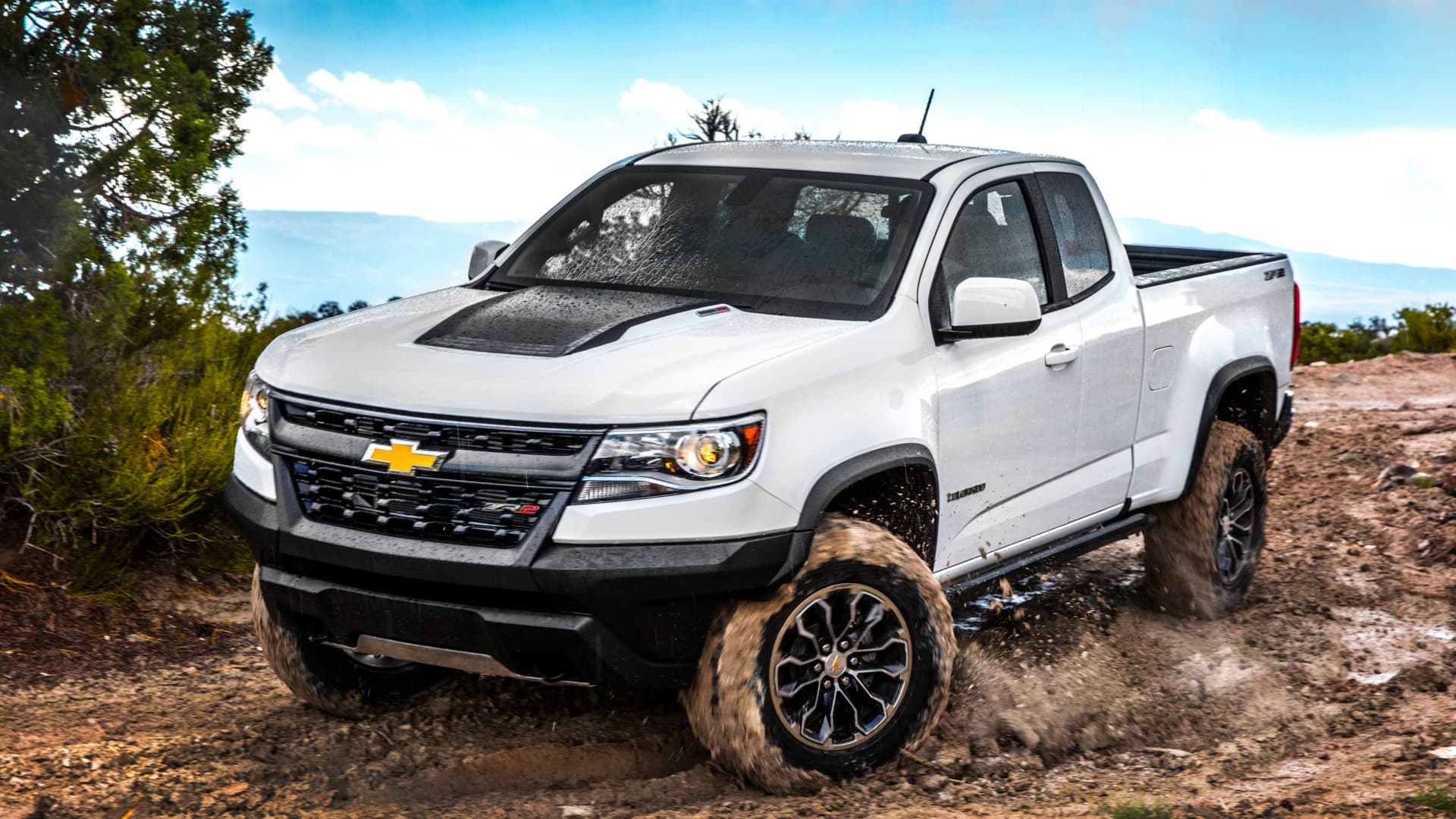
GM Defense was awarded a $214.3 million contract earlier this year by the Army to produce and maintain new Infantry Squad Vehicles, which are used to transport soldiers on battlefields. The company partnered on the contract with Ricardo Defense, which will lead product support for the vehicles.
The infantry vehicles are based off GM's Chevrolet Colorado ZR2 midsize truck and leverage 90% commercial off-the-shelf parts, which helps with development and production costs. But unlike the pickup for consumers, the ISVs are light and durable enough to be sling loaded and carried from a UH-60 Blackhawk helicopter.

"The reach back into GM is huge," Mark Dickens, GM Defense chief engineer, said during a recent media event. "That's the key enabler."
GM Defense's interim president, Tim Herrick, who also serves as GM vice president of global product programs, said the ISVs are "just the beginning" for the division. Ryder said other variants, including those with electric powertrains, are possible.
GM Defense has started renovating an existing building to support the production of the ISVs in North Carolina. The facility will help manufacture 649 ISVs and will support the production of up to 2,065 vehicles with additional authorization over eight years. The first vehicles delivered to the Army were built at GM's Milford Proving Grounds in Michigan.